Topography and Hydrology
Topography
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license.
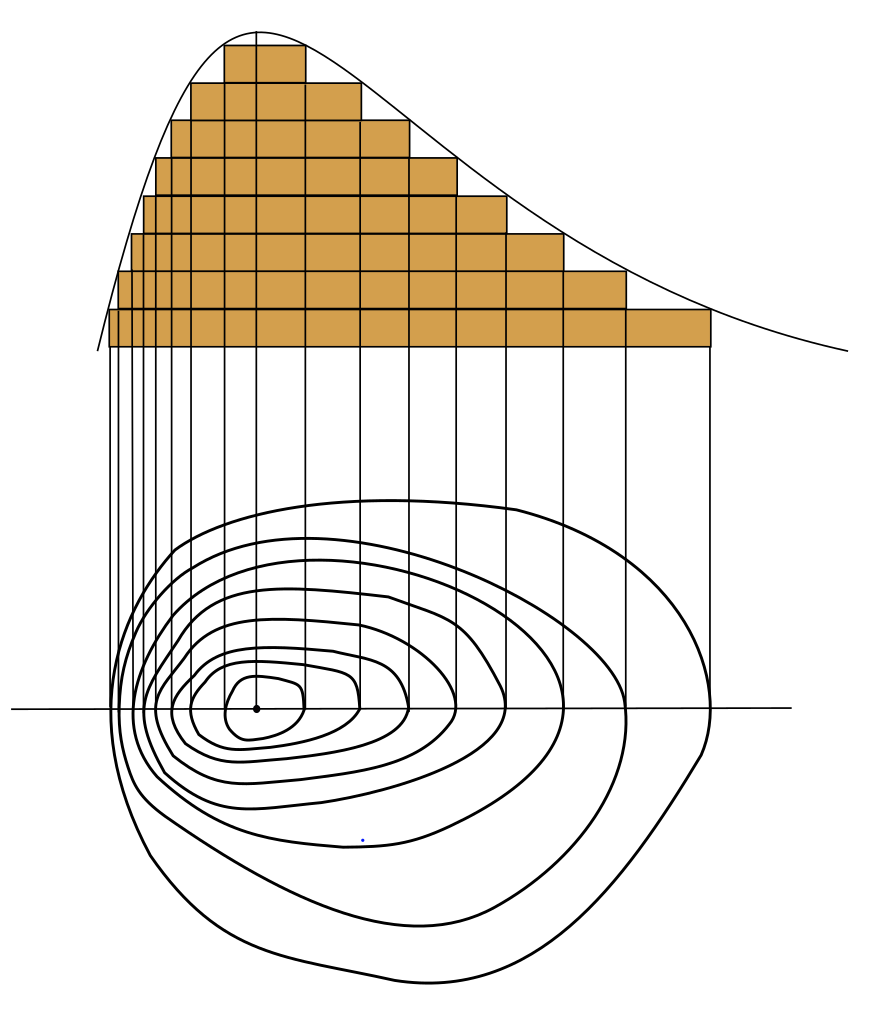
The topography of an area may refer to the landforms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps. Hydrologists use these topographic maps to determine the flow off a mountain or really from any region of higher ground eventually to the sea.
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, via Wikemedia Commons
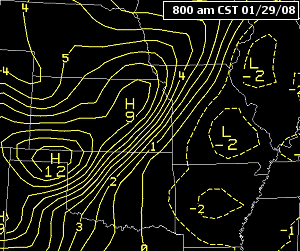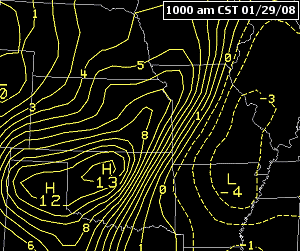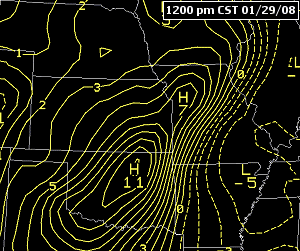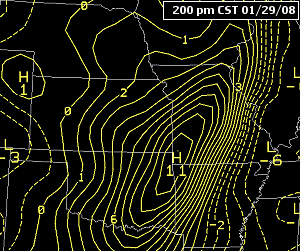
If there is a strong gradient between high pressure and low pressure the isobars (lines of constant pressure, at sea level) pack tighter together.
Tightly packed isobars are generally associated with stronger low-pressure systems, bringing at times stormy conditions and heavy rainfall.
Hydrology
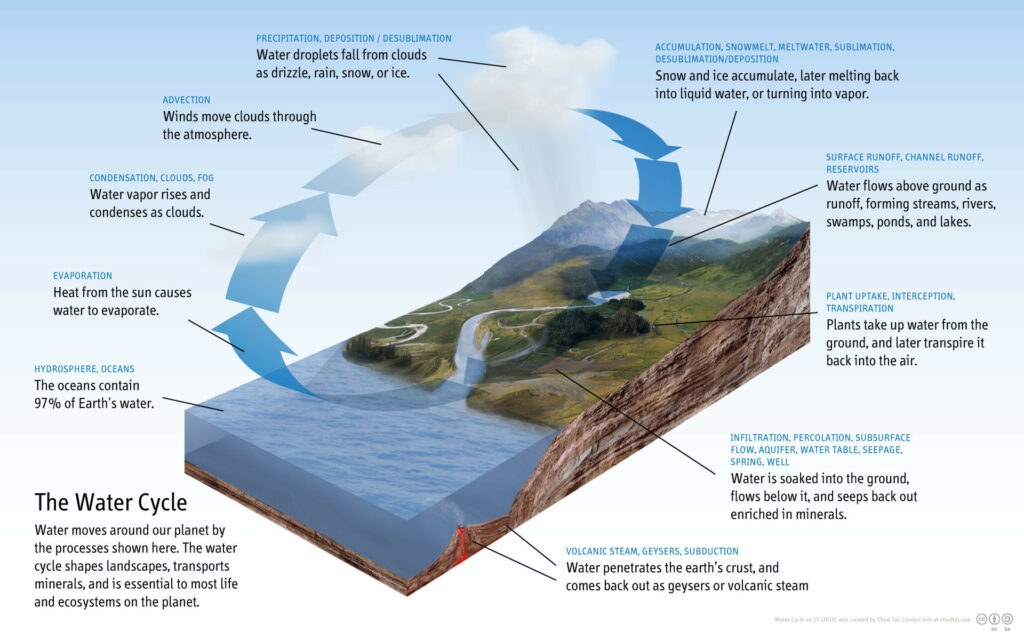
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International license.
The scientific study of the movement, distribution, and management of water on Earth and other planets, including the water cycle, water resources, and drainage basin sustainability.
It is important to be able to monitor water levels, predict flooding and forewarn drought conditions.
Hydrologists observe river, lakes and coastal seas monitoring how water bodies respond to rainfall and wind. To do this they need to know how much rainfall is going to fall and at what rate, as well as wind speeds for sea, swell and surge, from meteorological models.
They need to know how water will flow from higher ground to lower ground, where it will go, and at what speed.
By knowing the current conditions, they can then predict the effect on rivers, lakes and coastal regions while identifying hazards such as flooding, inundation, water shortages and drought risk.
Hydrology and Climate Change
While the overall climate outlook leans towards warmer drier conditions, individual events have the potential be more extreme, bringing torrential rainfall and violent winds and higher storm surge. Combined that with the potential for higher sea levels and the long-term risk to low lying coastal communities in particular is immense. However, the risk is far greater with the potential for more frequent droughts also. The extrema and blocking patterns will more frequently put intense pressure on the water supply systems, as well as flood defences, not to mention all the knock-on effects.
Hydrology and Farming.
Farming both relies upon and affect the overall hydrological system. Over drainage on farms can lead to a heightened risk of flooding downstream. While farmers reap the benefit of our naturally temperate and balanced climate, with some of the best grassland growth conditions in the world.
However, a more polarized climate will lead to much increased stresses on the land, crops and animals. Farming may have to adapt quickly to a changing climate to maintain successful production and mitigate downstream effects.